Evolving Role of Aortic Endografts in Aneurysm Repairs
28 Jul
2025
Highlights:
- Introduction
- Safer, Less Invasive Aneurysm Repair
- Advanced Designs for Complex Cases
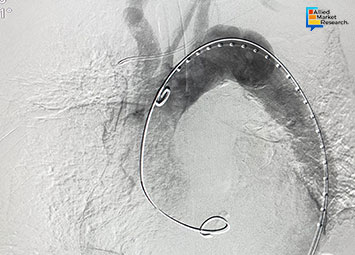
The treatment of aortic aneurysms has seen significant advancements over the past few years, especially with the growing use of aortic endografts. These devices have transformed the way clinicians approach aneurysm repairs. Unlike open surgical methods, endografts allow a minimally invasive route to fix weakened sections of the aorta. The core purpose is to prevent the risk of rupture by providing structural support within the artery.
Beyond Conventional Endograft DesignsThe standard use of endografts in abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair initially focused on patients with straightforward vascular structures. Over time, it became clear that not all patients present with favorable anatomy for a standard endovascular approach. This challenge has led manufacturers and clinicians to explore advanced configurations of endografts. Fenestrated and branched endografts have gained attention in this context. These devices are designed to accommodate vessels branching from the aorta, especially in cases of thoracoabdominal aneurysms. Customization in endograft designs has enabled the treatment of patients who were previously considered unsuitable for endovascular repair.
Recent studies and research contributions, such as those compiled by Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, emphasize that newer endograft systems are being developed with enhanced flexibility, sealing properties, and adaptability to tortuous vessels. The use of low-profile delivery systems and better conformability has created possibilities for treating a wider range of patients. Despite these improvements, the selection of an endograft still depends heavily on preoperative imaging and careful case planning. This ensures the right balance between device characteristics and patient-specific vascular conditions. According to Allied Market Research, the aortic endografts industry accounted for $3.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $6.2 billion by 2034, citing a CAGR of 6.3% during 2025-2034.
Aortic Endografts in the Context of Emerging TechniquesOne of the noteworthy trends in this field has been the growing interest in endovascular aneurysm sealing (EVAS) systems. Although the concept faced certain challenges due to reported complications in earlier devices, research is ongoing to assess its potential for specific patient groups. The main idea of EVAS is to fill the aneurysm sac with a polymer while anchoring the device to the healthy aorta. This differs from traditional endografts that rely solely on radial force and fixation at the vessel wall. While EVAS has not fully replaced standard endografts, it shows that innovation in this area remains active.
Another key development worth noting is the combination of endografts with adjunctive techniques like chimney grafts or parallel grafting. These approaches have emerged as solutions for situations where standard devices do not offer an adequate seal or when anatomical constraints make traditional deployment difficult. Clinical reports have suggested that while these hybrid techniques are technically demanding, they can offer viable options in high-risk cases.
Innovations on Advanced Endograft ApplicationsThe aortic repair segment witnessed notable developments in the past year, especially concerning clinical trials and device approvals. Cook Medical’s Zenith Fenestrated AAA Endovascular Graft recently received FDA approval for use in complex aneurysm cases, offering clinicians a dependable option for treating difficult anatomies. Additionally, Medtronic’s Valiant Navion thoracic stent graft system has received attention for its low-profile delivery mechanism, which enhances its reach in minimally invasive thoracic aortic repair. Although Medtronic voluntarily recalled the Valiant Navion device in 2021 due to performance concerns, the move showcases how closely the industry monitors post-market performance to ensure patient safety.
Apart from product launches, clinical research is investigating outcomes of using branched endografts in real-world settings. Studies published over the last two years have explored long-term patency, endoleak rates, and overall patient outcomes with newer graft systems. For example, Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine highlighted that the success of fenestrated endografts significantly depends on precise customization and operator experience, factors that directly influence procedural outcomes.
Summing upThe field of aortic endografts is driven by innovation aimed at addressing the growing complexity of vascular cases. Whether through design refinements, new materials, or advanced deployment techniques, the evolution of these devices is closely associated with clinical feedback and research findings. Manufacturers, clinicians, and researchers are playing an important role in refining how endografts are designed and used in practice. With advancements in technology, the primary focus is on improving patient outcomes, reducing complications, and broadening the range of patients who can benefit from less invasive aneurysm repair options.
Reach out to our team of experts for a clear and detailed understanding of the latest trends in the aortic endografts industry.
✍ **𝑨𝒓𝒕𝒊𝒄𝒍𝒆 𝒘𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒆𝒓: Koyel Ghosh

Koyel Ghosh
Author’s Bio- Koyel Ghosh is a blogger with a strong passion and enjoys writing in miscellaneous domains, as she believes it lets her explore a wide variety of niches. She has an innate interest in creativity and enjoys experimenting with different writing styles. A writer who never stops imagining, she has been serving the corporate industry for the last five years.
Avenue: Entire Library membership of Allied Market Research Reports at your disposal
- Avenue is an innovative subscription-based online report database.
- Avail an online access to the entire library of syndicated reports on more than 2,000 niche industries and company profiles on more than 12,000 firms across 11 domains.
- A cost-effective model tailored for entrepreneurs, investors, and students & researchers at universities.
- Request customizations, suggest new reports, and avail analyst support as per your requirements.
- Get an access to the library of reports at any time from any device and anywhere.
Related Post
-
How are Submarine Cables Transforming Global Connectivity with Enhanced User Experience?
-
Endoscopy Procedures: Transformations in Techniques and Applications
-
AI-Powered Video Analytics: How the Product Actually Works for enterprises
-
Painting Robots: Transforming Precision Coating and Creative Applications
-
Innovations in Pharmacovigilance Systems Advancing Patient Safety
-
Understanding Edge Security: Keeping Data Safe Near the Source
-
Exploring the Use and Advancements of 3D Laser Scanners in Professional Applications
-
Reinforcing Industrial Controls with Smarter Tools and Training








